HTTP
Scapy supports the sending / receiving of HTTP packets natively.
HTTP 1.X
Note
Support for HTTP 1.X was added in 2.4.3, whereas HTTP 2.X was already in 2.4.0.
About HTTP 1.X
HTTP 1.X is a text protocol. Those are pretty unusual nowadays (HTTP 2.X is binary), therefore its implementation is very different.
For transmission purposes, HTTP 1.X frames are split in various fragments during the connection, which may or not have been encoded. This is explain over https://developer.mozilla.org/fr/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/Transfer-Encoding
To summarize, the frames can be split in 3 different ways:
chunks: split in fragments called chunks that are preceded by their length. The end of a frame is marked by an empty chunkusing
Content-Length: the header of the HTTP frame announces the total length of the frameNone of the above: the HTTP frame ends when the TCP stream ends / when a TCP push happens.
Moreover, each frame may be additionally compressed, depending on the algorithm specified in the HTTP header:
compress: compressed using LZWdeflate: compressed using ZLIBbr: compressed using Brotligzip
Let’s have a look at what happens when you perform an HTTPRequest using Scapy’s TCP_client (explained below):
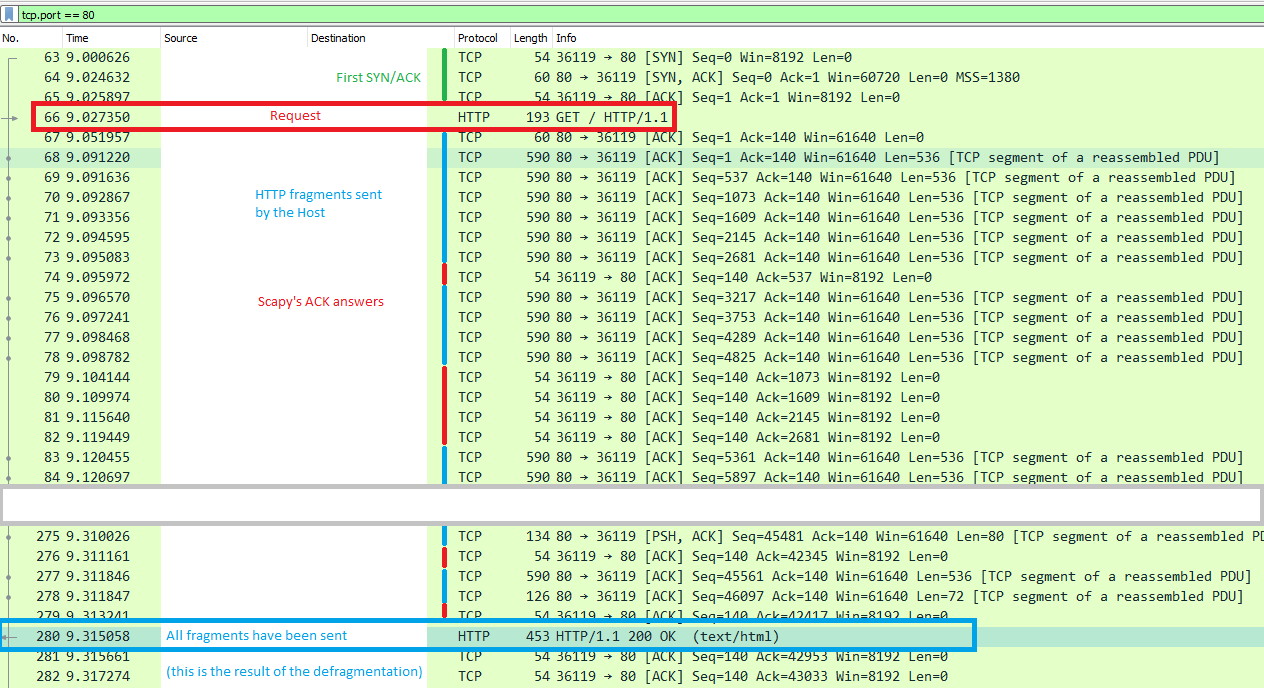
Once the first SYN/ACK is done, the connection is established. Scapy will send the HTTPRequest(), and the host will answer with HTTP fragments. Scapy will ACK each of those, and recompile them using TCPSession, like Wireshark does when it displays the answer frame.
HTTP 1.X in Scapy
Let’s list the module’s content:
>>> explore(scapy.layers.http)
Packets contained in scapy.layers.http:
Class |Name
------------|-------------
HTTP |HTTP 1
HTTPRequest |HTTP Request
HTTPResponse|HTTP Response
There are two frames available: HTTPRequest and HTTPResponse. The HTTP is only used during dissection, as a util to choose between the two.
All common header fields should be supported.
Default HTTPRequest:
>>> HTTPRequest().show()
###[ HTTP Request ]###
Method= 'GET'
Path= '/'
Http_Version= 'HTTP/1.1'
A_IM= None
Accept= None
Accept_Charset= None
Accept_Datetime= None
Accept_Encoding= None
[...]
Default HTTPResponse:
>>> HTTPResponse().show()
###[ HTTP Response ]###
Http_Version= 'HTTP/1.1'
Status_Code= '200'
Reason_Phrase= 'OK'
Accept_Patch43= None
Accept_Ranges= None
[...]
Use Scapy to send/receive HTTP 1.X
To handle this decompression, Scapy uses Sessions classes, more specifically the TCPSession class.
You have several ways of using it:
|
|
|---|---|
Perform decompression / defragmentation
on all TCP streams simultaneously, but
only acts passively.
|
Acts as a TCP client: handles SYN/ACK,
and all TCP actions, but only creates
one stream.
|
Examples:
TCP_client.tcplink:
Send an HTTPRequest to www.secdev.org and write the result in a file:
load_layer("http")
req = HTTP()/HTTPRequest(
Accept_Encoding=b'gzip, deflate',
Cache_Control=b'no-cache',
Connection=b'keep-alive',
Host=b'www.secdev.org',
Pragma=b'no-cache'
)
a = TCP_client.tcplink(HTTP, "www.secdev.org", 80)
answer = a.sr1(req)
a.close()
with open("www.secdev.org.html", "wb") as file:
file.write(answer.load)
TCP_client.tcplink makes it feel like it only received one packet, but in reality it was recombined in TCPSession.
If you performed a plain sniff(), you would have seen those packets.
This code is implemented in a utility function: http_request(), usable as so:
load_layer("http")
http_request("www.google.com", "/", display=True)
This will open the webpage in your default browser thanks to display=True.
sniff():
Dissect a pcap which contains a JPEG image that was sent over HTTP using chunks.
Note
The http_chunk.pcap.gz file is available in scapy/test/pcaps
load_layer("http")
pkts = sniff(offline="http_chunk.pcap.gz", session=TCPSession)
# a[29] is the HTTPResponse
with open("image.jpg", "wb") as file:
file.write(pkts[29].load)
HTTP 2.X
The HTTP 2 documentation is available as a Jupyter notebook over here: HTTP 2 Tuto